C++ is a high-performance, general-purpose programming language widely used for system programming, game development, competitive programming, and more. This C++ cheat sheet table provides a quick reference for essential syntax, concepts, and best practices.
On This Page
Table of Contents
C++ Cheat Sheet Table: Quick Reference Guide
| Concept | Syntax / Keyword | Example / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hello, World! | #include <iostream> / std::cout << "Hello"; | std::cout for output, std::cin for input. |
| Data Types | int, float, char, double, bool, string | int age = 25;, float pi = 3.14;, bool flag = true; |
| Variable Declaration | type variable_name = value; | Example: int x = 10; |
| Constants | const type variable = value; | Example: const double PI = 3.14159; |
| Operators | +, -, *, /, %, ++, -- | Arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, ternary. |
| Conditional Statements | if, else, switch | Example: if (x > 10) {} else {} switch (x) { case 1: break; } |
| Loops | for, while, do-while | Example: for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {} |
| Functions | returnType functionName(parameters) {} | Example: int sum(int a, int b) { return a + b; } |
| Function Overloading | Same name, different parameters | Example: int add(int, int); double add(double, double); |
| Inline Functions | inline returnType functionName() {} | Improves performance for small functions. |
| Recursion | Function calling itself | Example: int factorial(int n) { if (n==0) return 1; return n * factorial(n-1); } |
| Pointers | int* ptr = &var; | * (dereference), & (address-of operator). |
| Memory Allocation | new, delete | int* p = new int; delete p; |
| References | int &ref = variable; | Aliases for existing variables. |
| Arrays | int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5}; | Access with arr[index]. |
| Vectors (STL) | #include <vector> | std::vector<int> v; v.push_back(10); |
| Strings (STL) | #include <string> | std::string name = "John"; |
| Structs | struct StructName {} | Example: struct Car { string brand; int year; }; |
| Classes & Objects | class ClassName {} | Example: class Car { public: string brand; int year; }; |
| Encapsulation | private, public, protected | Restrict access to data members. |
| Constructors & Destructors | ClassName(), ~ClassName() | Initialize and clean up resources. |
| Inheritance | class Derived : public Base {} | Enables reusability of code. |
| Polymorphism | virtual, override | Example: virtual void function(); |
| Function Templates | template <typename T> | Generic functions for any data type. |
| Exception Handling | try, catch, throw | Example: try { throw "Error!"; } catch (const char* msg) {} |
| Lambda Functions | [](){} | Example: auto sum = [](int a, int b) { return a + b; }; |
| File Handling | #include <fstream> | Example: std::ofstream file("text.txt"); file << "Hello"; |
| Multithreading | #include <thread> | std::thread t(functionName); t.join(); |
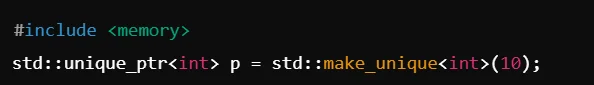
| Smart Pointers | std::unique_ptr, std::shared_ptr | Manages dynamic memory safely. |
| Bit Manipulation | &, ` | , ^, ~, <<, >>` |
| Macros | #define | Example: #define PI 3.14 |
| Namespace | namespace name {} | Example: namespace Math { int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } } |
| Enumerations | enum class Color {Red, Green, Blue}; | Strongly typed enums. |
| Command Line Arguments | int main(int argc, char* argv[]) | Used to handle input parameters. |
Wrap UP
C++ is a versatile language offering powerful tools for high-performance applications. This cheat sheet serves as a quick reference for mastering fundamental and advanced concepts, from basic syntax to object-oriented programming, memory management, and STL.
Keep this guide handy for coding interviews, competitive programming, and daily development. 🚀

Check Out our other Cheat Sheet-
- Markdown Cheatsheet
- Pyhton Cheatsheet
- Javascript Cheatsheet
- CSS Cheatsheet
- Java Cheatsheet
- HTML Cheatsheet
FAQs
What is C++?
C++ is a high-level, general-purpose programming language that supports object-oriented, procedural, and generic programming paradigms. It is widely used for system programming, game development, and competitive coding.
What are the key features of C++?
– Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
– Strongly Typed Language
– Standard Template Library (STL)
– Memory Management with Pointers
– Exception Handling
– Multi-threading Support
What is the difference between C and C++?
C is a procedural programming language, while C++ supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. C++ also has additional features like classes, inheritance, polymorphism, and STL.
What is a Class in C++?
A class is a user-defined blueprint for creating objects. It encapsulates data members (variables) and methods (functions) within a single unit.
Example:class Car {
public:
string brand;
int year;
};
What is an Object in C++?
An object is an instance of a class. It holds actual values for the class properties.
Example:Car myCar;
myCar.brand = "Toyota";
myCar.year = 2020;
What is Inheritance in C++?
Inheritance allows one class (child class) to derive properties and behaviors from another class (parent class).
Example:class Vehicle {
public:
int speed;
};
class Car : public Vehicle {
public:
string brand;
};
What is Polymorphism in C++?
Polymorphism allows the same function to have different behaviors. It can be achieved using function overloading and function overriding.
Example:class Animal {
public:
virtual void sound() {
cout << "Animal makes a sound";
}
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void sound() override {
cout << "Dog barks";
}
};
What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation is the bundling of data and functions into a single unit (class) and restricting direct access to data using access specifiers (private, public, protected).
What are the Access Specifiers in C++?
public: Accessible from anywhereprivate: Accessible only within the classprotected: Accessible within the class and derived classes
What is a Constructor in C++?
A constructor is a special function that initializes objects of a class. It has the same name as the class and does not return a value.
Example:class Car {
public:
Car() { cout << "Car is created"; }
};
What is a Destructor in C++?
A destructor is a special function that is automatically called when an object goes out of scope. It is used to free resources.
Example:class Car {
public:
~Car() { cout << "Car is destroyed"; }
};
What is a Pointer in C++?
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable.
Example:int x = 10;
int* ptr = &x;
What is a Reference in C++?
A reference is an alias for an existing variable.
Example:int x = 10;
int& ref = x;
What is Function Overloading?
Function overloading allows multiple functions with the same name but different parameters.
Example:int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
double add(double a, double b) { return a + b; }
What is Operator Overloading?
Operator overloading allows defining custom behaviors for operators.
Example:class Complex {
public:
int real, imag;
Complex operator + (const Complex& obj) {
Complex res;
res.real = real + obj.real;
res.imag = imag + obj.imag;
return res;
}
};
What is the Standard Template Library (STL)?
STL is a collection of reusable data structures and algorithms in C++. It includes:
– Containers (vector, list, map, set)
– Algorithms (sort, search)
– Iterators
Example: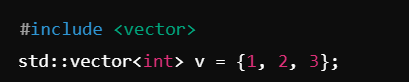
What is the Difference Between new and malloc()?
new is a C++ operator, while malloc() is a C function.new calls the constructor, malloc() does not.new returns a typed pointer, malloc() returns void*.
What is Exception Handling in C++?
Exception handling allows handling runtime errors using try, catch, and throw.
Example:try {
throw "An error occurred";
} catch (const char* msg) {
cout << msg;
}
What is a Virtual Function?
A virtual function allows function overriding in derived classes, ensuring dynamic (runtime) polymorphism.
Example:
class Base {
public:
virtual void show() { cout << "Base class"; }
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void show() override { cout << "Derived class"; }
};
What is a Smart Pointer in C++?
A smart pointer (std::unique_ptr, std::shared_ptr) manages dynamic memory automatically.
Example: